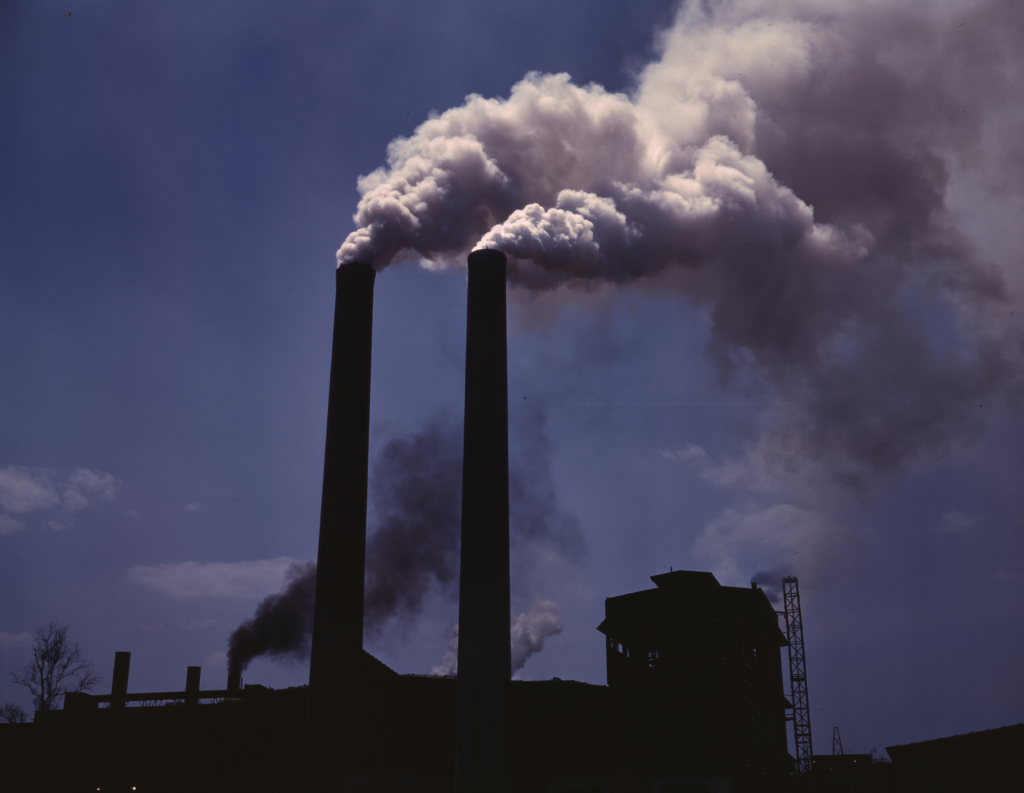
Air pollution is a pressing environmental issue that has far-reaching implications for human health, ecosystems, and the planet as a whole. This article explores the various aspects of air pollution, its causes, effects, and potential solutions.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Types of Air Pollutants
- Major Sources of Air Pollution
- Health Impacts of Air Pollution
- Environmental Effects
- Indoor Air Quality
- Measures to Reduce Air Pollution
- Government Policies and Regulations
- Technological Innovations
- The Role of Individuals
- Air Quality Index (AQI) Explained
- Global Initiatives to Combat Air Pollution
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Access Now: https://bit.ly/J_Umma
Introduction
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air, reaching levels that can negatively affect living organisms and the environment. It’s a complex issue that arises from various natural and human-made sources. The consequences of air pollution are wide-ranging and can impact everything from respiratory health to climate change.
Types of Air Pollutants
Air pollutants can be categorized into several groups: particulate matter (PM), ground-level ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants can come from both natural sources, such as wildfires and volcanic eruptions, and human activities like industrial processes and transportation.
Major Sources of Air Pollution
Human activities are the primary contributors to air pollution. Industries, vehicles, power generation, and agriculture release pollutants into the atmosphere. Burning fossil fuels is a major source of pollutants like CO2 and NO2. Deforestation also plays a role, as trees help filter the air.
Health Impacts of Air Pollution
Air pollution has serious health effects, particularly on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Short-term exposure can lead to breathing difficulties, while long-term exposure has been linked to conditions like asthma, lung cancer, and heart disease. Vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly are especially at risk.
Environmental Effects
Air pollution doesn’t just affect humans; it also harms ecosystems. Acid rain, a result of sulfur dioxide emissions, damages forests, bodies of water, and soil quality. Pollutants can disrupt the balance of ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and decreased agricultural productivity.
Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality is equally important. Indoor pollutants like mold, tobacco smoke, and household cleaning chemicals can lead to various health issues. Proper ventilation and reducing the use of harmful chemicals are crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality.
Measures to Reduce Air Pollution
Addressing air pollution requires a multi-faceted approach. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving public transportation, and implementing stricter emissions standards for industries are effective strategies. Investing in green technologies and encouraging sustainable practices are vital steps as well.
Government Policies and Regulations
Governments worldwide are enacting policies and regulations to curb air pollution. These can include emission standards for vehicles and industries, promoting clean energy, and setting air quality targets. Strong enforcement and cooperation between countries are essential for meaningful change.
Technological Innovations
Technology plays a pivotal role in combating air pollution. Innovations like electric vehicles, air purifiers, and cleaner industrial processes are helping to reduce emissions. Additionally, advancements in air quality monitoring provide real-time data to track pollution levels.
The Role of Individuals
Individuals can contribute by making conscious choices such as using public transport, reducing energy consumption, and recycling. Raising awareness about air pollution and advocating for sustainable practices can drive positive change on a larger scale.
Air Quality Index (AQI) Explained
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a standardized measure used to communicate air quality to the public. It considers various pollutants and categorizes air quality into ranges from “good” to “hazardous.” This information helps people make informed decisions about outdoor activities.
Global Initiatives to Combat Air Pollution
Various international organizations and agreements are working to tackle air pollution. The Paris Agreement, for example, aims to limit global warming and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Collaborative efforts like these are vital to address a problem that transcends national borders.
Conclusion
Air pollution is a complex and urgent challenge that requires global cooperation and action. By understanding its causes, effects, and potential solutions, we can work towards cleaner air, better health, and a sustainable future for generations to come.