The ozone layer is a crucial component of Earth’s atmosphere, playing a vital role in protecting life on our planet from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted by the sun. However, over the past few decades, the ozone layer has been facing significant depletion, raising concerns about its impact on human health, ecosystems, and the environment as a whole. In this article, we’ll delve into the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to ozone layer depletion.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Ozone Layer
- Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion
- Human Activities and Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- Natural Ozone Depleting Substances
- Ozone-Depleting Potential of Halons
- Consequences of Ozone Layer Depletion
- Increased UV Radiation Exposure
- Impact on Human Health
- Effects on Marine Ecosystems
- Agricultural Implications
- The Montreal Protocol: A Step Towards Recovery
- The Role of International Cooperation
- Innovations in Ozone-Friendly Technologies
- Alternative Refrigerants and Aerosol Propellants
- Solar-Powered Technologies
- Public Awareness and Education
- Government Policies and Regulations
- Conclusion
Introduction
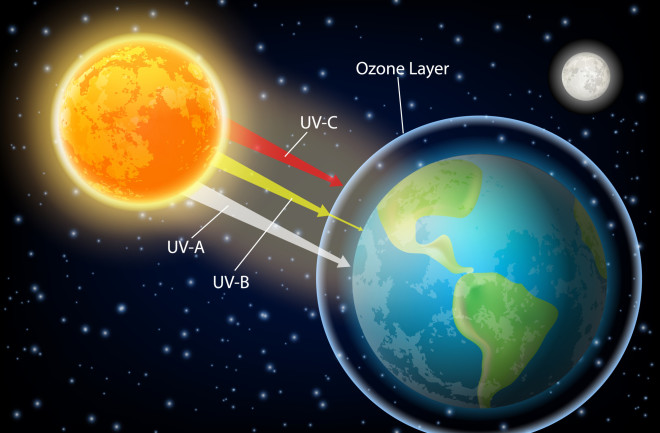
The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, acts as a shield against the most harmful UV rays from the sun, which can cause skin cancer, cataracts, and other health issues. However, the advent of industrialization introduced various substances that have led to ozone layer depletion.
Understanding the Ozone Layer
The ozone layer is primarily composed of ozone (O3) molecules, which form a protective layer around the Earth. This layer absorbs the majority of the sun’s harmful UV-B and UV-C radiation.
Causes of Ozone Layer Depletion
Human Activities and Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Human activities, such as the use of CFCs in refrigerants, solvents, and aerosol propellants, release chlorine and bromine compounds into the atmosphere. These compounds break down ozone molecules, leading to the thinning of the ozone layer.
Natural Ozone Depleting Substances
Apart from human-made substances, certain natural processes also release ozone-depleting substances into the atmosphere. For instance, volcanic eruptions release chlorine and bromine, contributing to ozone layer depletion.
Ozone-Depleting Potential of Halons
Halons, commonly used in fire extinguishers, contribute to ozone depletion as they contain bromine and chlorine. Even though their atmospheric concentration is lower, they have a much higher ozone-depleting potential.
Consequences of Ozone Layer Depletion
Increased UV Radiation Exposure
With a weakened ozone layer, higher levels of UV radiation reach the Earth’s surface, leading to an increase in skin cancer cases and other UV-related health issues.
Impact on Human Health
Ozone layer depletion has been linked to a rise in skin cancer, cataracts, and weakened immune systems. UV radiation can also cause sunburn and premature aging of the skin.
Effects on Marine Ecosystems
UV radiation can penetrate the ocean’s surface and harm marine life, including phytoplankton, which forms the basis of the marine food chain. This disruption can have cascading effects on aquatic ecosystems.
Agricultural Implications
Increased UV radiation can negatively affect crops, leading to reduced agricultural productivity. This can disrupt food supply chains and have economic ramifications.
The Montreal Protocol: A Step Towards Recovery
In 1987, the international community came together to sign the Montreal Protocol, which aimed to phase out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances. The protocol’s success highlights the importance of global cooperation in addressing environmental challenges.
The Role of International Cooperation
International collaboration and agreements are essential in combating ozone layer depletion. Continued efforts to enforce and strengthen regulations can ensure a healthier future for our planet.
Innovations in Ozone-Friendly Technologies
Alternative Refrigerants and Aerosol Propellants
Innovations in technology have led to the development of alternative refrigerants and aerosol propellants that have a lower ozone-depleting potential. These advancements play a significant role in reducing the impact of human activities on the ozone layer.
Solar-Powered Technologies
The adoption of solar-powered technologies reduces the reliance on energy sources that emit ozone-depleting substances. This transition not only benefits the ozone layer but also contributes to sustainable energy practices.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the importance of the ozone layer and its depletion is crucial. Education campaigns can encourage individuals to make environmentally conscious choices in their daily lives.
Government Policies and Regulations
Governments worldwide need to implement and enforce strict policies and regulations that limit the production and use of ozone-depleting substances. Financial incentives and penalties can drive industries toward more eco-friendly practices.
Conclusion
The depletion of the ozone layer is a serious environmental issue with far-reaching consequences. However, through international cooperation, technological innovation, public awareness, and strong governmental actions, we can mitigate the damage and ensure a healthier future for generations to come.