Introduction
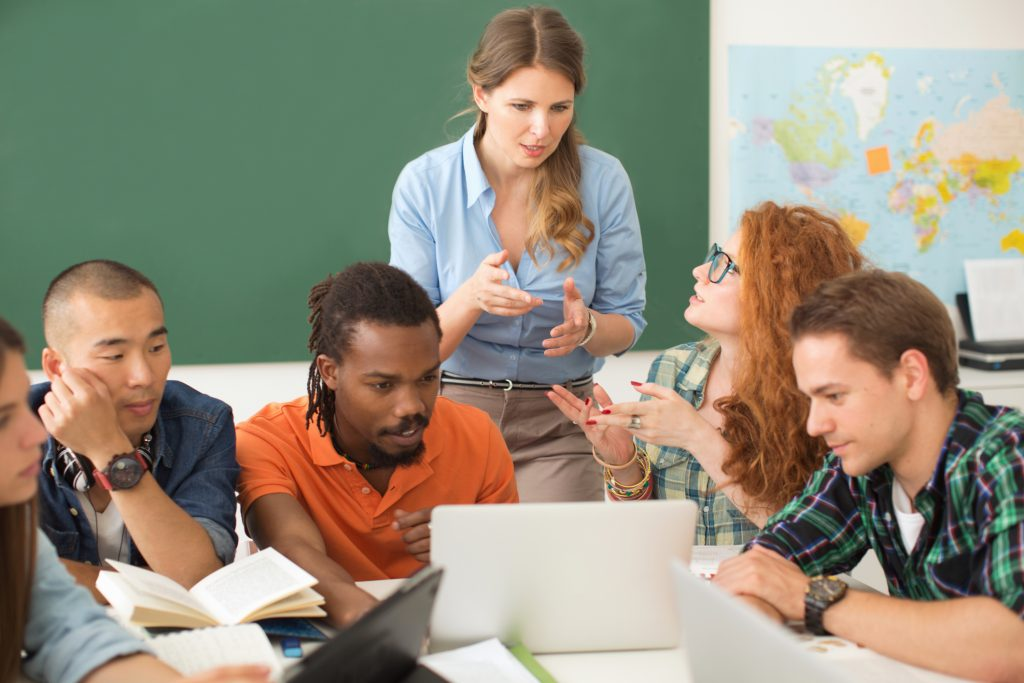
In the pursuit of a fair and equitable society, inclusivity in learning environments stands as a cornerstone. This analysis delves into the imperative of providing education for all, exploring the challenges, strategies, and transformative potential of fostering inclusivity in the educational landscape. From diverse student populations to accessible resources, addressing inclusivity ensures that education becomes a universal right rather than a privilege.
1. Understanding Inclusivity in Education
Inclusivity in education transcends the concept of mere access. We explore how it involves creating an environment that embraces diversity in all its forms, including race, ethnicity, gender, socioeconomic status, and abilities. Understanding the depth of inclusivity lays the foundation for building educational systems that cater to the needs of every learner.
2. The Challenge of Socioeconomic Inequality
Socioeconomic disparities pose a significant barrier to inclusivity in education. We delve into the challenges faced by individuals from low-income backgrounds, exploring how limited access to resources, educational materials, and extracurricular activities perpetuates inequality. Addressing socioeconomic inequality becomes a crucial step in fostering inclusivity.
3. Cultural Sensitivity and Diversity
Cultural sensitivity is essential for creating an inclusive learning environment. We explore how acknowledging and celebrating cultural diversity enhances the educational experience for all students. Integrating cultural sensitivity into curriculum design and teaching practices fosters an atmosphere where every student feels valued and understood.
4. Gender Equality in Education
Gender equality is a fundamental aspect of inclusivity. We delve into how gender biases and stereotypes can impact educational opportunities. Promoting gender equality involves creating environments where both male and female students have equal access to resources, encouragement, and educational pathways.
5. Accessibility for Individuals with Disabilities
Inclusivity demands accessibility for individuals with disabilities. We explore the challenges faced by students with diverse abilities and examine how adaptive technologies, accessible facilities, and tailored teaching methods contribute to an inclusive learning environment. Ensuring accessibility guarantees that education is a viable option for all learners.
6. Language Diversity and Inclusive Practices
Language diversity can be a barrier to effective learning. We delve into how inclusive practices accommodate students with different linguistic backgrounds. Recognizing the importance of multilingual approaches and providing language support ensures that language does not become a hindrance to education.
7. Creating Inclusive Curriculum and Teaching Methods
Inclusivity should be embedded in the very fabric of curriculum design and teaching methods. We explore how creating inclusive curriculum materials and employing diverse teaching strategies cater to various learning styles and preferences. Developing inclusive approaches ensures that every student can actively engage with the educational content.
8. Addressing Bias and Discrimination
Bias and discrimination within educational institutions hinder inclusivity. We delve into how acknowledging, addressing, and rectifying bias contribute to a more inclusive learning environment. Implementing policies and practices that actively combat discrimination ensures that every student feels safe and supported.
9. Parental and Community Involvement
Inclusivity extends beyond the classroom to involve parents and the broader community. We explore how fostering collaboration between educators, parents, and community members enriches the educational experience. Engaging parents and the community ensures a collective effort in creating an inclusive and supportive learning environment.
10. Utilizing Technology for Inclusive Education
Technology can be a powerful tool for inclusivity. We delve into how leveraging educational technology, online resources, and digital tools can bridge gaps and provide access to diverse learning opportunities. Utilizing technology ensures that education transcends physical boundaries, reaching students in remote or underserved areas.
Conclusion
Education for all is not just an ideal; it is a fundamental right that must be actively pursued. By addressing inclusivity in learning environments through diverse strategies, we create a space where every individual can thrive, regardless of background, ability, or circumstance. Fostering inclusivity in education is not only a moral imperative but a crucial step toward building a society where every voice is heard and every learner has the opportunity to reach their full potential.