Have you ever wondered how your vegetables maintain their vibrant colors and crisp textures when you enjoy them in a variety of dishes? The answer lies in a culinary technique known as blanching. In this article, we’ll delve into the art of blanching, exploring its benefits, methods, and practical applications. Whether you’re a seasoned chef or an aspiring home cook, understanding blanching can take your culinary creations to the next level.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Blanching
- The Science Behind Blanching
- Step-by-Step Guide to Blanching
- Gathering Your Ingredients
- Prepping and Cleaning the Produce
- Boiling the Water
- Blanching the Produce
- Cooling and Drying the Produce
- Blanching in Different Cuisines
- The Benefits of Blanching
- Preserving Color and Texture
- Inactivating Enzymes
- Retaining Nutrients
- Blanching vs. Other Cooking Methods
- Boiling
- Steaming
- Creative Applications of Blanching
- Conclusion
Introduction to Blanching
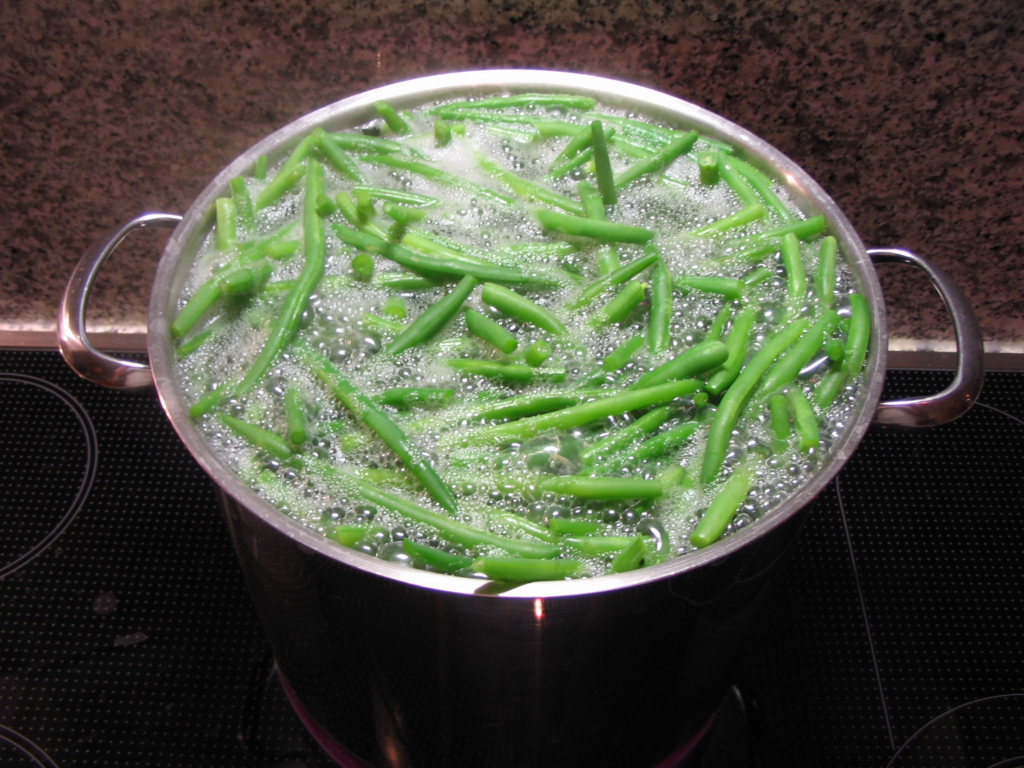
Blanching is a culinary process that involves briefly immersing vegetables, and sometimes even fruits, into boiling water and then rapidly cooling them in ice water. This technique serves multiple purposes, from enhancing color retention to neutralizing enzymes that could otherwise cause the produce to deteriorate over time.
The Science Behind Blanching
The science behind blanching revolves around the enzymes present in fruits and vegetables. These enzymes can lead to undesirable changes in color, flavor, and texture. By blanching, you halt the activity of these enzymes, ensuring that your produce remains fresher for longer periods.
Step-by-Step Guide to Blanching
Gathering Your Ingredients
Before you begin blanching, ensure you have fresh, high-quality produce that is ready to undergo the process. Choose vegetables that are at their peak ripeness for the best results.
Prepping and Cleaning the Produce
Wash the produce thoroughly to remove any dirt or contaminants. You may also need to trim or cut the vegetables into suitable sizes, depending on your intended use.
Boiling the Water
Fill a pot with water and bring it to a rolling boil. You can add a pinch of salt to enhance the flavor of the blanched produce.
Blanching the Produce
Carefully add the prepared vegetables to the boiling water. Allow them to cook for a brief period, usually just a few minutes, until they become slightly tender but still retain their crispness and vibrant color.
Cooling and Drying the Produce
Once blanched, promptly transfer the vegetables to a bowl of ice water. This halts the cooking process and preserves the color and texture. After a few minutes, remove the produce from the ice water and allow them to dry before using them in your dishes.
Blanching in Different Cuisines
Blanching is a technique that spans across various culinary traditions. In Asian cuisines, blanching is often used as a preliminary step before stir-frying, ensuring that the vegetables are tender yet retain a delightful crunch. Similarly, blanching is utilized in Mediterranean cuisine to prepare vegetables for salads while preserving their vibrant hues.
The Benefits of Blanching
Preserving Color and Texture
One of the primary benefits of blanching is the preservation of color and texture. Your vegetables remain visually appealing and maintain a pleasant bite, enhancing the overall dining experience.
Inactivating Enzymes
Blanching’s ability to inactivate enzymes is crucial in preventing the loss of flavor and nutritional value that can occur over time. This process extends the shelf life of your produce.
Retaining Nutrients
Unlike some cooking methods that can lead to nutrient loss, blanching is relatively gentle and helps retain essential vitamins and minerals in your vegetables.
Blanching vs. Other Cooking Methods
Boiling
While blanching and boiling both involve water, blanching requires a shorter cooking time. Boiling might lead to more nutrient loss and could result in overcooked vegetables.
Steaming
Steaming is another popular cooking method, but blanching can be advantageous when you want to stop the cooking process quickly and preserve the color and crunch of the vegetables.
Creative Applications of Blanching
Blanching isn’t just reserved for plain vegetables. You can blanch tomatoes to make peeling easier for sauces, or blanch almonds to remove their skins effortlessly. The possibilities are vast and can add a touch of finesse to your culinary repertoire.
Conclusion
Blanching is a valuable technique in the culinary world that ensures your vegetables and certain fruits maintain their visual appeal, texture, and nutritional value. By understanding the science and process behind blanching, you can elevate your cooking skills and create dishes that are as vibrant and flavorful as they are nutritious. So, whether you’re preparing a colorful salad or a delightful stir-fry, don’t underestimate the power of blanching in creating truly exceptional meals.