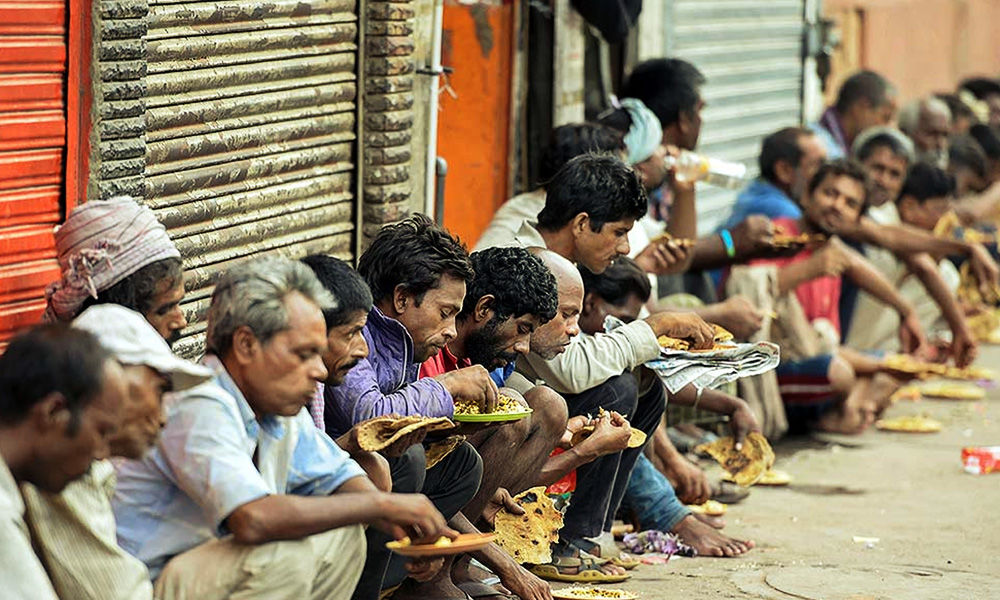
Poverty is a pervasive global issue that affects millions of individuals and families. It’s not just about lacking financial resources; it encompasses a lack of access to basic necessities, education, healthcare, and opportunities. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of poverty, its underlying causes, far-reaching consequences, and potential solutions.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Defining Poverty
- Causes of Poverty
- Structural Inequality
- Lack of Education
- Unemployment and Underemployment
- Limited Access to Healthcare
- Gender Discrimination
- Consequences of Poverty
- Health Disparities
- Limited Education Opportunities
- Cycle of Generational Poverty
- Social Exclusion
- Increased Crime Rates
- Breaking the Chains: Solutions to Poverty
- Education Initiatives
- Skill Development Programs
- Microfinance and Small Business Support
- Healthcare Access Improvement
- Social Safety Nets
- Global Efforts to Combat Poverty
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and Charities
- Government Policies and Welfare Programs
- Changing Mindsets: Overcoming Stereotypes
- The Role of Privilege and Empathy
- Community Empowerment and Grassroots Movements
- Conclusion
Introduction
Poverty is not solely about a lack of financial resources; it encompasses a multifaceted deprivation of basic human needs and opportunities. Understanding its underlying causes and addressing its consequences is crucial for creating a more just and equitable society.
Defining Poverty
Poverty can be defined as the state of living with insufficient material possessions or income to meet basic human needs. These needs include food, clean water, shelter, clothing, and access to education and healthcare. However, poverty’s impact goes beyond the material realm, affecting mental and emotional well-being.
Causes of Poverty
Structural Inequality
Structural inequality, stemming from unequal distribution of resources and opportunities, plays a significant role in perpetuating poverty. Marginalized communities often face systemic barriers that limit their access to education, jobs, and social mobility.
Lack of Education
Education is a powerful tool for breaking the cycle of poverty. However, limited access to quality education, especially in developing countries, can trap individuals in low-income jobs and prevent upward mobility.
Unemployment and Underemployment
Lack of job opportunities or being stuck in underpaid, unstable jobs can lead to a life of poverty. It also hinders economic growth at both individual and societal levels.
Limited Access to Healthcare
Poor healthcare access further deepens poverty’s impact. Medical expenses can push families into financial ruin, perpetuating the cycle of poverty.
Gender Discrimination
Women and girls often face disproportionate poverty due to gender discrimination. Limited access to education and job opportunities keeps them economically vulnerable.
Consequences of Poverty
Health Disparities
Poverty is closely linked to health inequalities. Limited access to nutritious food and healthcare results in higher rates of diseases among impoverished populations.
Limited Education Opportunities
Children from impoverished backgrounds often lack access to quality education. This limits their potential and perpetuates intergenerational poverty.
Cycle of Generational Poverty
Poverty’s grasp can extend across generations. Children born into impoverished families face limited opportunities, continuing the cycle.
Social Exclusion
Poverty can lead to social exclusion, limiting participation in community activities and reinforcing feelings of hopelessness.
Increased Crime Rates
In areas with high poverty rates, crime rates often surge as individuals turn to illegal means for survival.
Breaking the Chains: Solutions to Poverty
Education Initiatives
Investing in education, especially for marginalized communities, can break the cycle of poverty. Scholarships, school meals, and educational infrastructure are vital components.
Skill Development Programs
Equipping individuals with vocational skills enhances their employability, empowering them to secure better-paying jobs.
Microfinance and Small Business Support
Microfinance initiatives provide financial services to those who lack access to traditional banking, allowing them to start small businesses and improve their livelihoods.
Healthcare Access Improvement
Expanding healthcare services and implementing financial assistance programs can alleviate the healthcare burden on impoverished families.
Social Safety Nets
Government-led social safety net programs, such as unemployment benefits and food assistance, provide a safety cushion for vulnerable populations.
Global Efforts to Combat Poverty
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
The UN’s goals include eradicating extreme poverty and hunger, emphasizing international cooperation to address this global issue.
NGOs and Charities
Numerous organizations work tirelessly to alleviate poverty’s effects by providing resources, education, and healthcare to marginalized communities.
Government Policies and Welfare Programs
Governments play a crucial role through policies that promote equitable access to education, healthcare, and job opportunities.
Changing Mindsets: Overcoming Stereotypes
Shifting societal attitudes is essential. Eradicating poverty requires recognizing the dignity and potential of every individual.
The Role of Privilege and Empathy
Those in positions of privilege can contribute by raising awareness, supporting initiatives, and advocating for policy changes that address poverty’s root causes.
Community Empowerment and Grassroots Movements
Local initiatives and community-driven efforts can create a meaningful impact by addressing specific challenges within impoverished neighborhoods.
Conclusion
Poverty is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. By understanding its causes and consequences and implementing sustainable solutions, we can strive to create a world where every individual’s basic needs are met, and opportunities are accessible to all.