Introduction
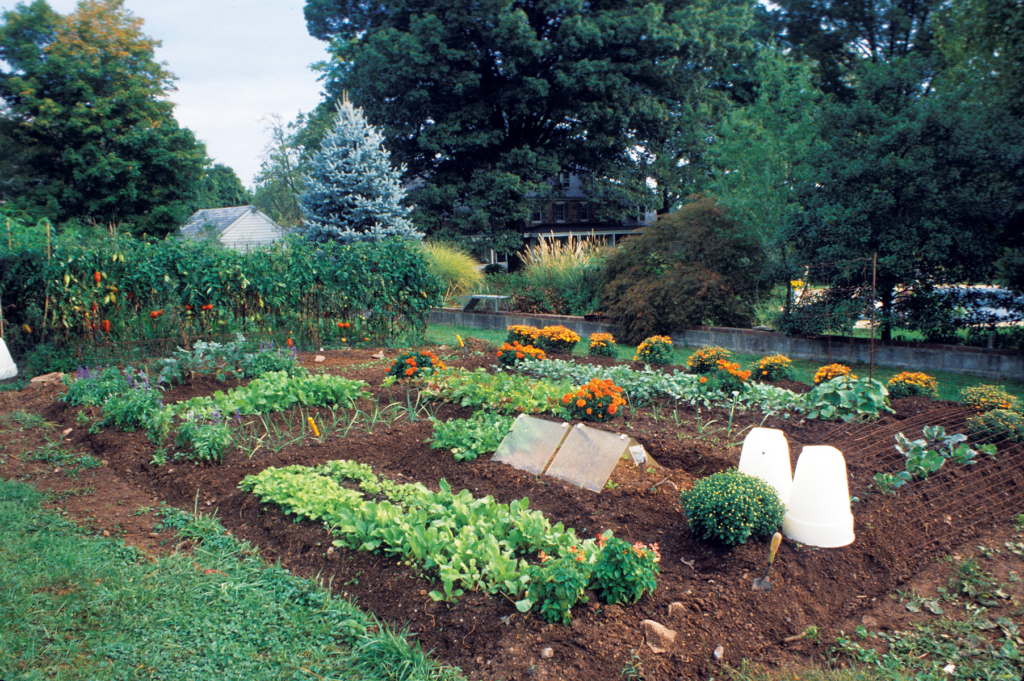

In the realm of agriculture and environmental stewardship, soil nurturing stands as a fundamental practice. With the well-being of our planet at the forefront of global concerns, understanding how to nurture and care for our soil is imperative. This article delves into the significance of soil nurturing, its benefits, and practical strategies to ensure the fertility and vitality of the land.
The Essence of Soil Nurturing
The Foundation of Sustainable Agriculture
Soil nurturing forms the backbone of sustainable agriculture. It involves holistic practices aimed at enriching the soil’s quality, structure, and nutrient content. This foundation is pivotal for long-term agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
Unraveling Soil Health
Soil Health: The Key to Abundant Harvests
Healthy soil is a treasure trove for farmers and gardeners alike. It’s teeming with a myriad of microorganisms, earthworms, and fungi that contribute to soil structure and nutrient cycling.
The Role of Soil Microbes
Microbes, invisible to the naked eye, play an essential role in soil health. They aid in breaking down organic matter, fixing nitrogen, and releasing essential nutrients for plants.
Benefits of Soil Nurturing
Enhanced Crop Yield and Quality
Optimizing Nutrient Availability
Through practices like composting and cover cropping, soil nurturing increases nutrient availability to plants. This results in higher crop yields and improved produce quality.
Resilience Against Pests and Diseases
Healthy soil nurtured through organic practices fosters robust plants that are more resistant to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Water Management and Conservation
Preventing Erosion and Runoff
A well-nurtured soil structure helps retain water, preventing erosion and runoff. This contributes to water conservation and prevents soil degradation.
Drought Mitigation
Healthy soil acts like a sponge, holding onto moisture during dry spells. This characteristic aids in mitigating the impacts of drought on crops.
Strategies for Effective Soil Nurturing
Cover Cropping and Green Manure
Harnessing Plant Diversity
Cover crops and green manure involve planting specific crops to enrich the soil between main crops. They enhance soil structure and add organic matter.
Nitrogen Fixation
Leguminous cover crops play a crucial role in fixing atmospheric nitrogen into the soil, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Composting: Nature’s Recycling
Creating Nutrient-Rich Compost
Composting kitchen scraps, yard waste, and organic matter creates nutrient-rich compost. This black gold enriches soil structure and fertility.
Microbial Activity
Compost is teeming with microbial life that contributes to soil health. It improves soil structure, aeration, and moisture retention.
Conclusion
Soil nurturing is more than a farming technique; it’s a commitment to the planet’s well-being. By understanding the intricate balance of soil health and adopting nurturing practices, we pave the way for sustainable agriculture and a healthier environment.